
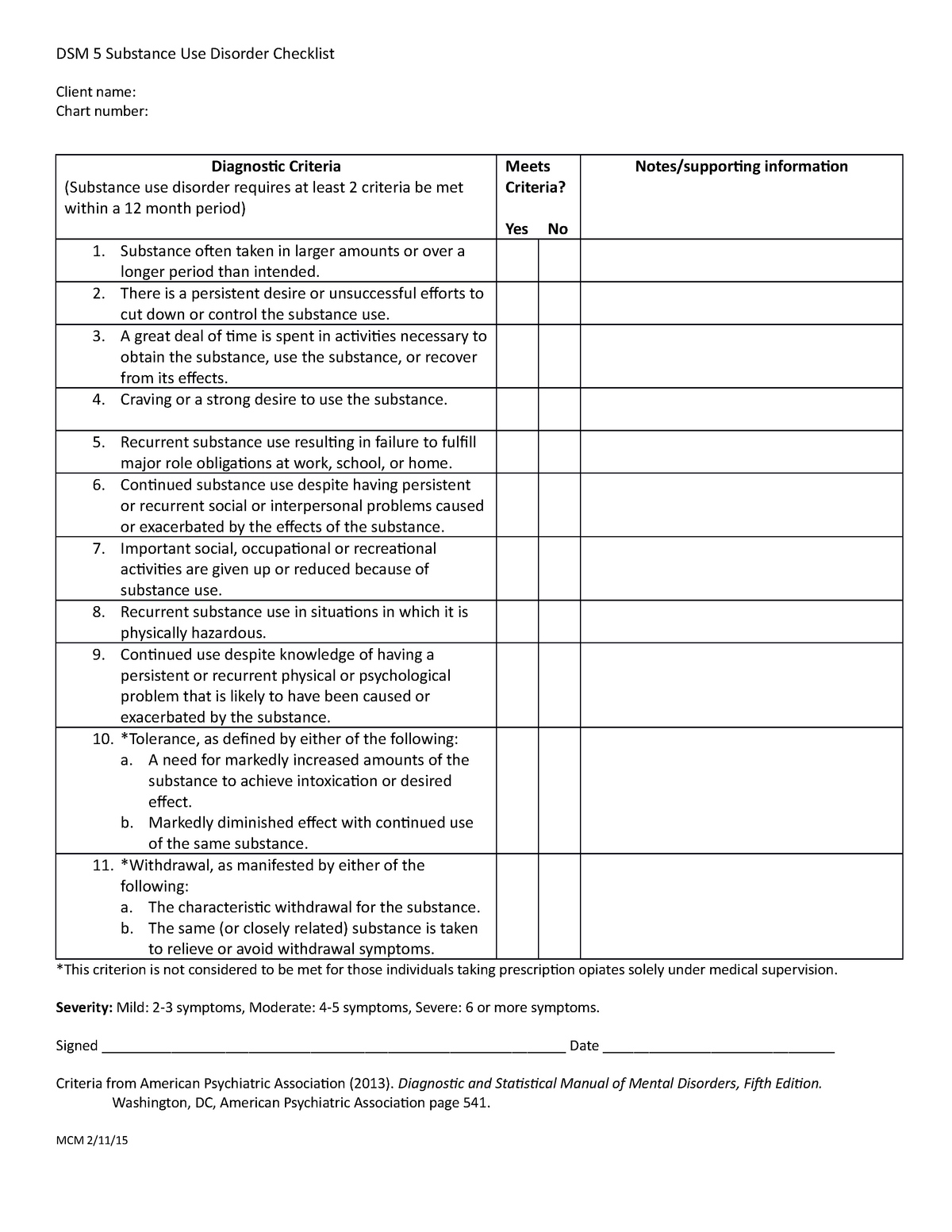
Continued use in the face of developing health problems.Risk-taking, such as using while driving.Continued use in spite of relationship conflicts.Investing large amounts of time obtaining substances.In order to be diagnosed with this disorder, a person must exhibit at least two of the following 11 symptoms within a 12-month period: Symptoms of DSM 5 substance use disorder develop out of the brain’ and body’s growing dependence on drug/alcohol effects. Symptoms of DSM 5 Substance Use DisorderĪ substance use disorder can lead to depression. If you’re considering treatment and you’re not sure if your insurance will cover your treatment costs, call our helpline atĨ0 ( Who Answers?) for more information. From there, the DSM 5 substance use disorder diagnosis delineates the key components of the condition. What most distinguishes substance use disorder from casual drug use lies in the effects drug use have on a person’s overall quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dsm-5-criteria-for-substance-use-disorders-21926_V2-c979cb0780134583bc6fa3a6f2315d63.png)
The diagnosis, substance use disorder first appeared in the third DSM edition in 1980 and has since undergone a few changes in its definition.
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER DSM 5 MANUAL
The “DSM V” designation indicates that this is the fifth edition of the manual with the first edition published in 1952, according to the American Journal of Psychiatry. DSM 5 Substance Use DisorderĭSM is an acronym for the Diagnostic Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders, a standard text used by mental health and drug treatment professionals. Once identified, it’s important to take the necessary steps to get treatment to prevent the effects of drug abuse from ruining your life. The features of DSM substance use disorder include symptoms of drug abuse as well as the adverse effects it has in a person’s daily life. While not everyone who uses drugs necessarily has a problem, certain key signs can help in determining whether a drug problem exists.ĭSM 5 substance use disorder encompasses a set of criteria that helps treatment professionals identify and treat people affected by substance abuse issues. These findings underscore the need for tailored treatment programs for those presenting with DSM-5 CUD, and for greater treatment specification where poly-drug use is evident.Rates of substance abuse have reached epidemic proportions over the last decade, destroying lives and families in the process. Newer-class illicit and prescription stimulant-based drug use disorders are overrepresented among those with DSM-5 CUD. High comorbidity exists between DSM-5 CUD and many specific DSM-5 SUDs. Current DSM-5 CUD is associated with greater lifetime use of all examined drug classes, and previous 12-month use of several newer-class illicit and prescription stimulant-based substances (all p0.05). Weighted cross-tabulations and multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to evaluate comorbidity between current DSM-5 CUD, substance use and DSM-5 SUD. 36,309 adults aged 18+ from wave 3 of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC-III) were assessed. This study therefore aimed to provide insight into the degree of these co-occurring relationships across several specific newer and older generation illicit and prescription drugs.

Cannabis use disorder (CUD) is frequently associated with concurrent substance use and/or comorbid substance use disorders (SUDs) however there is little specificity with regard to commonly abused individual drug types/classes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
